Scientists discover a new class of transferable tigecycline high-level resistance mechanisms
May 31, 2019 Source: Science Network
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];On May 28th, "Nature-Microbiology" magazine published a research paper entitled "Emergence of plasmid-mediated high-level tigecycline resistance genes in animals and humans" by the academic team of Academician Shen Jianzhong of China Agricultural University.
Tigecycline is the third generation of tetracyclines for human medicine developed by Wyeth in the United States. It was listed in China in 2011. The World Health Organization (WHO) listed it as an extremely important antibacterial agent for the treatment of clinical multi-drug resistant infections. Treatment of skin and skin tissue infections and complex intra-abdominal infections. In the current medical clinical multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria resistant to carbapenems, tigecycline and another peptide drug polymyxin have become the few treatments for the above infections. select. However, in recent years, the research team reported for the first time the production, transmission and risk analysis of the transferable polymyxin resistance gene mcr-1 (published in Lancet Infectious Disease 2016, 2017; Nature Microbiology 2018), making tigecycline already Become the "last line of defense" in the true sense of treating "superbug" infections.
In view of the importance of tigecycline in medical clinics, the academician Shen Jianzhong has been monitoring the resistance of tigecycline to important pathogens in recent years. Through unremitting efforts, the research team and the researchers of the Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences found a strain of Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli carrying the tet(X) gene variant in the pig source samples, and the encoded proteins were found separately. Wild type TetX has 85.1% and 93.8% homology, hence the names tet (X3) and tet (X4). Subsequently, the research team used functional cloning, protein tertiary structure prediction, molecular docking, and complemented by protease kinetics, mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance to verify the modification of tetracyclines by two new variants. 1).
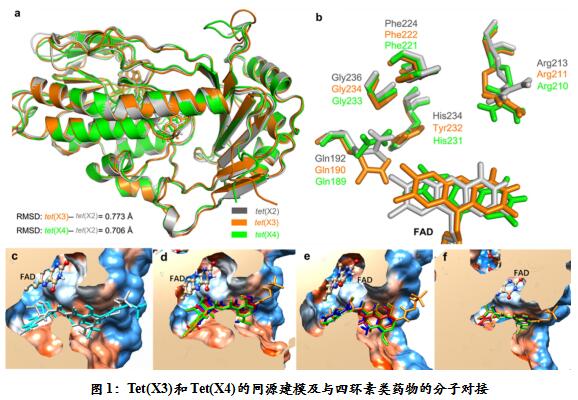
Compared to wild-type TetX, these two variants not only mediate high levels of resistance to tigecycline in wild strains (minimum inhibitory concentration is 32–64 mg l –1 ), but also mediate US food and drug High levels of resistance to two new tetracyclines, eravacycline and omadacycline, recently approved by the Authority. These two new drugs, as alternatives to tigecycline, have better antibacterial activity and minor side effects than tigecycline and are not currently available in the country. Gene transfer studies indicate that both tet (X3) and tet (X4) are located on the multi-drug resistant plasmid of bacteria and can be transferred into clinically important pathogens such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli by conjugation. . More importantly, animal models have demonstrated that tet(X) variants can lead to clinical failure of tigecycline to treat infections with pathogens carrying this class of resistance genes (Figure 2). Epidemiological retrospective investigation showed that the average detection rate of tet (X3) and tet (X4) in domestic animal and food-derived bacteria was 6.9%, and the detection rate of pig-derived E. coli in some areas reached 66.7%. And 5 strains of Acinetobacter sinensis carry the carbapenem resistance genes blaNDM-1 and tet (X3). In addition, the research team also detected tet(X4) from three human-medical clinical infections, Escherichia coli and one strain of Acinetobacter baumannii. Although the detection rate is low (0.07%), the risk cannot be ignored.
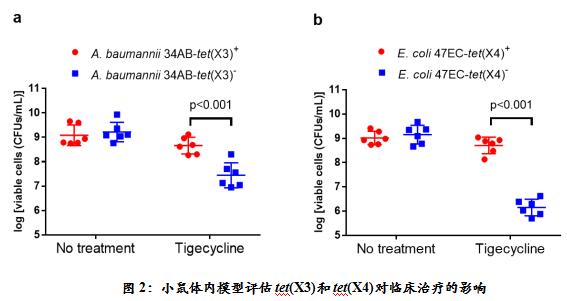
It is particularly important to note that these two new types of tet(X) variants also have cross-resistance and can mediate resistance to traditional first- and second-generation tetracyclines. At present, the first and second generation tetracyclines represented by chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and doxycycline are the most widely used antibacterial drugs in livestock and poultry breeding, and are widely used in the growth and prevention of livestock and poultry. Strong drug selection pressure may promote the enrichment and transfer of tet(X) variants and their carrying bacteria in livestock and poultry, and increase their possibility of transmission through the food chain or environment. Therefore, this study also played a warning role for the use of tetracyclines, especially chlortetracycline and oxytetracycline, as growth promoters in livestock and poultry farming. Further research should be conducted to evaluate the use of such drugs in food animals. risks of.
Dr. He Tao and Dr. Wang Wei from Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Liu Dejun, a postdoctoral fellow at China Agricultural University, are the co-first authors of this research paper; Professor of Animal Medicine, China Agricultural University, and Wang Yang, a post-scientist of Beijing Food Nutrition and Human Health Center And Academician Shen Jianzhong is the co-author of this article. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology's “13th Five-Year Plan†national key R&D program, the National Natural Science Foundation “China-UK†international cooperation project and the Ministry of Agriculture.
Related paper information: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0445-2
Black tea (dark tea) is named after the black appearance of the finished tea. It is one of the six major tea groups and is a post-fermented tea. The main production areas are Guangxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Hubei, Hunan, Shaanxi and Anhui. The traditional black tea is made from high maturity black wool tea, which is the main raw material for pressing tightly pressed tea.
The process of making black tea generally includes four steps: killing, kneading, stacking and drying. Black tea is mainly classified as Hunan black tea (Fu tea, Qianliang tea, black brick tea, Tri-tip, etc.), Hubei green brick tea, Sichuan Tibetan tea (border tea), Anhui Gu Yi black tea (An tea), Yunnan black tea (Pu'er tea), Guangxi Liubao tea and Shaanxi black tea (Fu tea) according to geographical distribution.
The yellow powder in black tea is commonly known as golden flower, a beneficial microorganism, the so-called golden flower, is in the processing of raw materials through the flowering of this special procedure, specifically in the black tea bricks to cultivate a kind of coronary aspergillus substance called coronary scattered cystic bacteria, commonly known as the golden flower, observed under the microscope, each individual golden flower is umbrella-shaped clusters, the whole body is golden and eye-catching, ringed into a group, evenly distributed.
Yunnan black tea powder ; Hubei black brick tea powderï¼›Pu'er tea power
Shaanxi Zhongyi Kangjian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zhongyibiology.com